Mushrooms are a fascinating and diverse group of organisms known for their various shapes, sizes, and colors. While we often associate mushrooms with earthy browns and whites, the truth is that mushrooms come in a wide range of captivating colors.
In this article, we will explore the different colors of mushrooms and the factors that influence their pigmentation. Understanding mushroom colors can be not only intriguing but also useful when it comes to choosing mushrooms for culinary purposes.
Let’s delve into the world of mushroom colors and discover the vibrant spectrum that mushrooms offer.
Mushrooms exhibit various colors, each with unique charm and characteristics. Some of the common colors include:
– White Mushrooms
– Brown Mushrooms
– Yellow Mushrooms
– Red Mushrooms
– Black Mushrooms
– Blue Mushrooms
– Green Mushrooms
– Purple Mushrooms
– Other Colorful Mushrooms
Several factors contribute to the pigmentation of mushrooms, including genetics, environment, age, and exposure to light. These factors combine to create the stunning palette of colors observed in mushrooms.
The color of mushrooms can provide valuable information about their flavor, culinary uses, and potential health benefits. By understanding the relationship between color and mushroom characteristics, one can make informed choices when selecting mushrooms for cooking or other purposes.
Join us on this journey as we explore the captivating world of mushroom colors and gain a deeper appreciation for the vibrant and diverse organisms that mushrooms are.
- The variety of mushroom colors is vast, including white, brown, yellow, red, black, blue, green, purple, and other colorful variations.
- Mushroom colors are influenced by genetics, environment, age, and exposure to light.
- Choosing mushrooms based on color can help determine flavor profiles and culinary uses.
The Variety of Mushroom Colors

Photo Credits: True2Mushrooms.Com by Philip Gonzalez
From snowy white to vibrant purple, the world of mushroom colors is a mesmerizing spectrum. In this journey through the various mushroom colors, we’ll uncover the fascinating hues that nature has gifted these extraordinary fungi.
Discover the allure of brown earthy mushrooms, the boldness of red caps, and even the surreal beauty of blue and green varieties. Get ready to explore the enchanting world of mushroom colors like never before!
White Mushrooms
White Mushrooms are a highly sought-after type of edible mushroom due to their pale, creamy white color. These mushrooms possess a mild flavor that effortlessly complements various ingredients. They offer a firm texture and a delicate taste.
White mushrooms can be utilized in many dishes, including stir-fries, soups, salads, and pasta dishes. It is easy to find these mushrooms in most grocery stores. The best part is that white mushrooms are low in calories and fat and packed with essential vitamins and minerals such as selenium and potassium.
Choosing firm ones with a clean surface is advisable when purchasing white mushrooms. Store them in the refrigerator using a paper bag or a breathable container to maintain their freshness.
Regarding cooking methods, white mushrooms can be sautéed, grilled, or roasted. They can be enjoyed raw in salads or used as a delightful topping for pizzas and sandwiches.
Brown Mushrooms
Brown mushrooms, such as cremini, portobello, and shiitake, are popular edible fungi. These mushrooms come in various sizes and flavors.
Cremini mushrooms are a delicious option with their light to dark brown color and mild, earthy flavor. Portobello mushrooms, conversely, are larger and more mature creminis, offering a meaty texture and rich taste. Meanwhile, shiitake mushrooms have a dark brown color, a firm texture, and a slightly smoky flavor.
Not only are brown mushrooms versatile but they can also be used in a wide range of dishes. You can sauté, grill, roast, or incorporate them into soups, sauces, stir-fries, and pasta dishes.
In addition to their culinary uses, brown mushrooms are also low in calories and fat, making them a healthy addition to your meals. They are packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including a rich source of B vitamins, selenium, and potassium.
When selecting the best brown mushrooms, choose firm and plump ones free from blemishes or mold. Avoid mushrooms that have a slimy texture or emit an unpleasant odor.
To preserve the quality and flavor, store your brown mushrooms in a paper bag in the refrigerator and consume them within a few days.
Yellow Mushrooms
Yellow mushrooms are vibrant and unique fungi. Here are some key facts about yellow mushrooms:
- Yellow mushrooms range in shades from pale yellow to deep golden hues.
- They are commonly found in forests and woodlands.
- Well-known species of yellow mushrooms include the Golden Chanterelle, Yellowfoot Chanterelle, and Yellow Knight mushroom.
- Yellow mushrooms have a distinct flavor profile, with some varieties offering a fruity or apricot-like aroma.
- Gourmet chefs highly prize yellow mushrooms for their taste and visual appeal.
- When cooked, yellow mushrooms maintain their vibrant color.
- Yellow mushrooms are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Due to their distinct color, yellow mushrooms are easy to identify in the wild.
- It is crucial to properly identify any wild mushroom before consuming it.
- Yellow mushrooms can be a great addition to stir-fries, pasta dishes, and soups.
Yellow mushrooms offer a visual delight and a unique culinary experience. Exploring the world of yellow mushrooms can be exciting and rewarding for adventurous eaters and nature enthusiasts.
Red Mushrooms
1. Red Cap
Red mushrooms have vibrant red caps that stand out among other mushrooms.
2. Poisonous Varieties
Not all red mushrooms are safe to eat. For example, the Amanita muscaria is highly toxic and can cause severe illness or even death if ingested.
3. Culinary Uses
Although many red mushrooms are poisonous, a few edible varieties can be used in cooking. One example is the red-capped white mushroom (Russula brevipes), which has a mild flavor and pairs well with various dishes.
4. Identification
Before consuming red mushrooms, it is crucial to identify the species correctly. Consulting an expert or using reputable field guides can help ensure you’re picking safe and edible mushrooms.
Black Mushrooms
Black Mushrooms, such as Black Morel, Black Trumpet, and Black Chanterelle, boast a deep hue and a distinct, earthy taste. These mushrooms elevate risotto flavors, pasta sauces, stir-fries, and soups. They possess an eye-catching aesthetic that makes them ideal for garnishing or plating.
Blue Mushrooms
| Type of Mushroom | Description | Common Examples |
| Blue Mushrooms | Blue mushrooms are a unique variety known for their distinctive blue color. The color ranges from pale blue to dark blue and can be found on the cap, stem, or both. | Blue Chanterelle, Indigo Milk Cap, Blue Crust |
Blue mushrooms are a rare type of fungus that attracts nature enthusiasts. These mushrooms have a stunning blue color, ranging from pale to deep blue, which makes them visually appealing. The blue hue can be found on the cap, stem, or both.
Some examples of blue mushrooms found in nature include Blue Chanterelle, Indigo Milk Cap, and Blue Crust. Each variety has its unique characteristics, including the distinct blue color. Blue mushrooms highlight the diversity and beauty of fungi.
Various factors like genetics and light exposure influence the blue color in these mushrooms. Scientists are studying the specific pigment responsible for the blue coloration. Chemical compounds present in these mushrooms contribute to their vivid blue appearance.
When encountering blue mushrooms in the wild, it’s important to exercise caution and seek expert knowledge for proper identification. Some blue mushrooms may be toxic, while others are edible and prized for their unique flavors and culinary uses.
Green Mushrooms
| Green Mushrooms | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Green Chanterelles |
| 2 | Green Cup Mushrooms |
| 3 | Green Toadstools |
| 4 | Green Fairy Ring Mushrooms |
Green mushrooms come in different species, such as Green Chanterelles, Green Cup Mushrooms, Green Toadstools, and Green Fairy Ring Mushrooms. They have a vibrant green color caused by specific pigments or environmental factors, making them visually appealing and great for adding color to dishes.
The presence of green mushrooms in an area may indicate the availability of specific nutrients or environmental conditions that support their growth. Not all green mushrooms are safe, as some may be toxic. It is important to consult a mushroom expert or reliable resources for mushroom identification before consuming any wild mushrooms.
If you encounter green mushrooms in the market or while foraging, consider using them in your culinary creations. They can add a unique flavor and texture to various dishes, but cook them thoroughly for safety and proper digestion.
Always prioritize food safety and choose mushrooms from reputable sources to minimize the risk of consuming potentially harmful varieties. Explore the world of mushrooms and experiment with different colors to enhance your culinary experiences.
Purple Mushrooms
Purple mushrooms, such as the Amethyst Deceiver and Purple Cortinarius, are visually striking fungi in various regions worldwide. These fungi come in shades from deep violet to lavender or lilac.
Some edible varieties of purple mushrooms, like the Blue-foot or Tawny Funnel, can even be incorporated into gourmet dishes, adding a pop of color. These mushrooms can provide an earthy, nutty, or slightly sweet flavor when consumed.
In addition to their unique taste, purple mushrooms are also rich in antioxidants, offering potential health benefits.
If you’re feeling adventurous, try incorporating purple mushrooms into pasta dishes, risottos, or sautés for a delicious and visually appealing meal. Please remember to identify and cook mushrooms before consumption to ensure safety properly.
Enjoy the experience of experimenting with these rare and beautiful purple fungi!
Other Colorful Mushrooms
Yellow Morels, Pink Oyster Mushrooms, Orange Chanterelles, Blue Chanterelles, Purple Coral Mushrooms, Red Cage Fungi, Green Russulas, Rainbow Lactarius, and Black Trumpets are some of the other colorful mushrooms that can be incorporated into culinary creations.
These vibrant fungi add visual appeal to dishes and bring unique flavors and textures to recipes.
Mushroom enthusiasts are particularly drawn to the yellow color of Yellow Morels, the pink hue of Pink Oyster Mushrooms, the orange color of Orange Chanterelles, the blue color of Blue Chanterelles, the deep purple color and intricate shape of Purple Coral Mushrooms, the bright red color and distinctive cage-like structure of Red Cage Fungi, the vibrant green color of Green Russulas, the array of colors ranging from yellow to orange to green in Rainbow Lactarius, and the dark brown to black color of Black Trumpets.
Each mushroom offers a distinct flavor profile that can enhance various dishes. From the nutty flavor of Yellow Morels to the mild and slightly sweet taste of Pink Oyster Mushrooms, these mushrooms can be used in savory and sweet recipes.
The fruity and peppery flavor of Orange Chanterelles pairs well with various ingredients, while the earthy flavor of Blue Chanterelles complements both meat and vegetarian dishes.
Purple Coral Mushrooms add a mild and nutty flavor to stir-fries, soups, and pasta dishes.
Red Cage Fungi, with their slightly peppery taste, can be used as a decorative element in salads or as a dish garnish. The mild and slightly nutty flavor of
Green Russulas make them versatile in salads, sautés, or soups. With its mild and slightly fruity flavor, Rainbow Lactarius is often used in stir-fries and risottos.
Despite their name, Black Trumpets are dark brown to black and have a rich, smoky flavor that pairs well with meats. These colorful mushrooms elevate culinary creations, offering delightful flavors and textures. Experimenting with these vibrant fungi can add color and excitement to any dish.
Factors Influencing Mushroom Colors
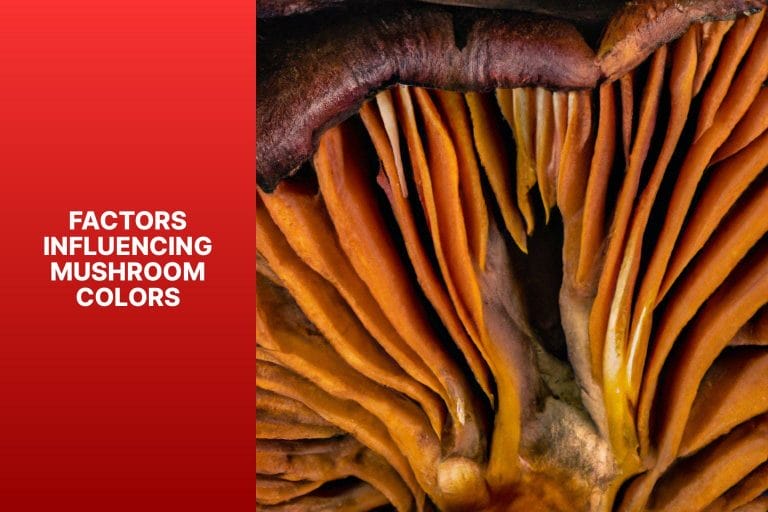
Photo Credits: True2Mushrooms.Com by Nathan Young
Regarding the captivating world of mushroom colors, various factors come into play. This section will explore the intriguing influences behind these vibrant hues.
From genetics to the environment, age, and even exposure to light, each sub-section will uncover the secrets that shape the mesmerizing colors we encounter in mushrooms.
So, get ready to dive into the captivating interplay of factors contributing to the fascinating spectrum of mushroom shades.
Genetics
Genetics determine mushroom color. Genes in mushroom DNA produce pigments like melanin, carotenoids, and anthocyanins, giving mushrooms their colors.
Mushroom color comes from parent spores, with variations from genetic mutations. White mushrooms result from pigment production inhibition. Brown mushrooms have melanin pigments.
Complex genetic makeup determines mushroom color range. Multiple genes produce pigments, which environmental factors can influence. This creates color variations.
Genetics is significant, but environmental conditions, age, and light exposure impact mushroom color. When categorizing mushrooms by color, consider genetics and external factors.
Environment
Environment influences mushroom color. Factors related to the environment that affect mushroom color include:
1. Light Exposure: The amount and intensity of light a mushroom receives affects its color. Direct sunlight can result in darker pigments, while shaded areas produce lighter-colored mushrooms.
2. Humidity: Mushrooms thrive in moist environments. Higher humidity levels can produce fungi with brighter and more vibrant colors, while drier conditions may lead to paler-colored mushrooms.
3. Temperature: Different temperature ranges impact mushroom pigmentation. Some species display more vivid colors in cooler temperatures, while others become more vibrant in warmer conditions.
4. Soil Composition: The soil composition where mushrooms grow can impact their color. Certain minerals and nutrients in the soil can affect pigment production, resulting in color variations.
5. Microbial Interactions: Mushrooms have symbiotic relationships with bacteria and fungi. These interactions can influence pigment production and, in turn, the colors of mushrooms.
Considering the environment when selecting mushrooms can add diversity to your culinary experiences and allow you to explore the different flavors and textures associated with various colors. Experiment with mushrooms in your dishes and discover how their environment contributes to their unique qualities.
Age
Mushroom colors can vary depending on factors like age. The age of a mushroom can affect its color development. Here’s a table showing the relationship between mushroom age and color:
| Age | Color |
| Young | Lighter shades, like pale white or light brown |
| Mature | Darker shades, like deep brown or black |
| Overripe | Discoloration may occur, such as yellowing or browning |
As mushrooms age, their pigments can change due to the breakdown of color compounds. Young mushrooms have lighter shades, while mature mushrooms develop darker colors. Overripe mushrooms can show signs of discoloration, indicating deterioration.
Considering mushroom age is important when choosing them for cooking. Young mushrooms are often preferred for their delicate flavor and tender texture. Mature mushrooms have a stronger taste and firmer texture, making them suitable for certain dishes.
When selecting mushrooms based on color, it’s important to consider the color variations that can occur as mushrooms age. The desired color can contribute to the presentation and taste of a dish.
Exposure to Light
Exposure to light plays a significant role in impacting both the color and nutritional content of mushrooms. The presence of light triggers the production of pigments that are responsible for the vibrant colors of mushrooms.
Mushrooms exposed to light during their growth tend to have lighter shades, whereas those grown in dark or shaded areas appear darker. It is worth noting that the duration and intensity of light exposure also contribute to color variation.
When exposed to prolonged or direct sunlight, mushrooms exhibit more vivid and vibrant colors—conversely, limited light exposure results in dull or pale colors in mushrooms.
Light exposure influences the nutritional value of mushrooms. Sunlight is a natural vitamin D source, which mushrooms can synthesize when exposed to sunlight. This makes mushrooms an excellent dietary source of this essential vitamin for humans.
It is interesting to delve into the ancient beliefs surrounding mushrooms. In ancient times, mushrooms were regarded as possessing mystical properties and were often associated with supernatural beings.
Certain cultures even believed that mushrooms could only grow in places where they received divine light, thus making them sacred for religious rituals. The light was and still is perceived as a symbol of purity and enlightenment.
Although our understanding of mushrooms has evolved, the significance of light in their growth and development remains a captivating aspect of their biology.
Choosing Mushrooms Based on Color

Photo Credits: True2Mushrooms.Com by Zachary Hernandez
Exploring the world of mushrooms is like diving into a palette of colors! This section delves into the fascinating realm of choosing mushrooms based on color.
Get ready to uncover how different mushroom colors can influence their distinct flavors and culinary uses. Whether you’re a curious foodie or a seasoned chef, understanding the relationship between color and mushrooms will open up a new world of gastronomic possibilities.
Let’s embark on this colorful journey together!
Color and Flavor
I found red mushrooms in the forest. Their vibrant color intrigued me, so I cooked them and discovered their flavor was unexpectedly robust and peppery. The red mushrooms enhanced the dish’s taste with a unique and spicy kick.
It was a delightful culinary experience, revealing endless flavor possibilities of different mushroom colors. Since then, I have been more open to experimenting with various colored mushrooms, as each hue brings its distinct flavor profile to the table.
Color and Culinary Uses
| Color | Culinary Uses |
|---|---|
| White | Used in soups, sauces, and stir-fries. Mild flavor and delicate texture. |
| Brown | They are preferred for sautéing and grilling: robust flavor and meaty texture. Great in risottos and stews. |
| Yellow | Common in Asian cuisine. Adds mild earthy flavor. Stir-fried or added to noodle dishes. |
| Red | They are not commonly used in cooking due to toxicity. Most red mushrooms are poisonous. |
| Black | Highly prized in Eastern European and Asian cuisines. Rich, umami flavor. Popular in soups, stews, and braised dishes. |
| Blue | Rare and not commonly consumed and not typically used in culinary applications due to its unusual color. |
| Green | Rare, but it can be used similarly to other mild-flavored mushrooms. Sometimes added to salads or used as a garnish. |
| Purple | Visually striking but not commonly used in cooking. Some varieties are edible but limited culinary uses. |
| Other Colorful Mushrooms | Various flavors and culinary uses depend on the specific variety. Research each type before using it in recipes. |
When using mushrooms in cooking, consider their color, indicating their flavor profile, texture, and suitability for different dishes. Experimenting with various mushroom colors adds depth and variety to culinary creations.
Some Facts About Mushroom Color:
- ✅ Mushroom color is a popular neutral hue for home decor. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ It is considered a warm and neutral tone, a mixture of beige and gray. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Mushroom color can enhance the living space when incorporated as accents. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Mushroom paint colors are versatile and can be used on walls, furniture, and exteriors. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Lighting and decor can affect how mushroom paint colors look in a specific space. (Source: Our Team)


